Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a neuro-vascular syndrome which refers to three related syndromes involving compression of the nerves, arteries, and veins in the lower neck and upper chest. The diagnostic tests described below are not very specific and are only of limited diagnostic value. If the patient complains of vague shoulder pain with tingling of the arm, the tests described below can be used to assess whether one of the following syndromes are involved:
- Scalenus syndrome.
- Costo-clavicular compression syndrome (CCCS).
- Hyper-abduction syndrome.
Before carrying out the tests, the radial artery should be palpated bilaterally.
Adson’s Test
During this test, the inter-scalene space will be made smaller, causing increased compression of the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus (particularly C8 and T1) against the first rib.
Procedure
- Bring the patient’s outstretched arm backwards in retroflexion and adduction, and palpate the radial artery.
- Ask the patient turn their head to the homo-lateral side, whilst stretching the neck as much as possible.
- Support this movement with your other hand.
- Ask the patient to inhale and hold their breath for a short period [Figure 58].
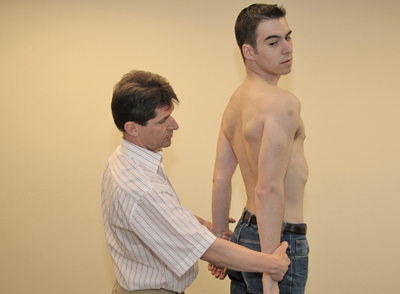 Figure 58
Figure 58
- Repeat the test with the head turned to the hetero-lateral side [Figure 59].
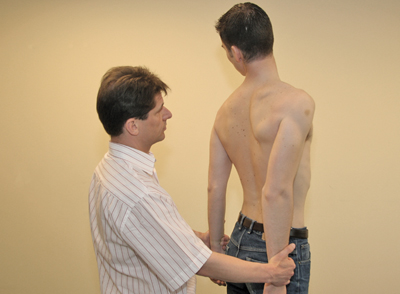 Figure 59
Figure 59
Pay attention to a reduction or possible absence of the radial pulse, and note whether signs of neurological irritation are evoked or aggravated. The test is positive if both above mentioned phenomena occur in step 2/step 5 and the result for the contralateral side is negative.
Costoclavicular Manoeuvre (Military Brace)
During this test, the cluster of blood vessels and nerves in the costoclavicular space may be compressed.
Procedure
- Ask the patient to move the shoulder(s) backwards and downwards.
- The examiner can, if necessary, exert further traction on the patient’s arm(s) [Figure 60].
- Palpate the radial artery (bilaterally).
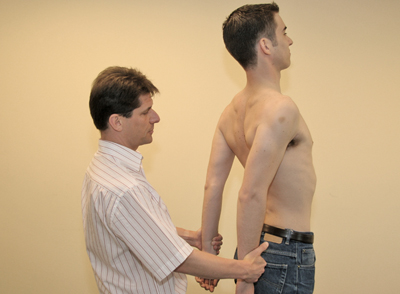 Figure 60
Figure 60
Note any reduction or possible absence of radial pulse, and whether signs of neurological irritation are evoked or aggravated. The test is positive if both above mentioned phenomena occur and the result for the contralateral side is negative.
Hyperabduction Manoeuvre (Wright’s Test)
During this test, the cluster of blood vessels and nerves (subclavian artery and vein of the brachial plexus) can be compressed at the following locations:
- Between the coracoid process and pectoralis minor muscle on one side and the thoracic wall on the other side.
- Between the first rib and the clavicle (during abduction of the arm, the clavicle turns around the longitudinal axis, during which the curve of the clavicle can cause compression).
Procedure
- Ask the patient to abduct and rotate their arm(s) outwards.
- Support this movement if necessary [Figure 61].
- Palpate the radial artery (bilaterally).
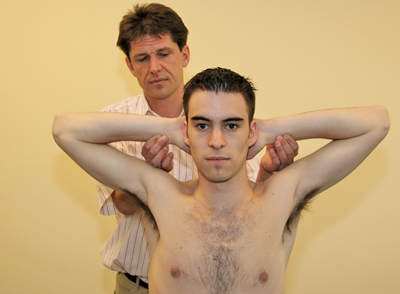 Figure 61
Figure 61
Pay attention to a reduction or possible absence of the radial pulse, and note whether any signs of neurological irritation are evoked or aggravated. The test is positive if both above mentioned phenomena occur and the result for the contralateral side is negative.




























