Location of the lungs and airways in relation to the thoracic wall
The lungs are located in the thoracic cavity. To describe the lung boundaries or when indicating the position of the (abnormal) examination findings, anatomical landmarks are used.
These landmarks are:
Anteriorly
horizontal (Figure 1)
- supraclavicular fossa (space above the collarbone)
- clavicle (collarbone)
- infraclavicular fossa (space beneath the collarbone)
- sternal angle (angle of Louis: junction of the sternal manubrium and the body of the sternum, attachment point to the 2nd rib)
Not indicated in Figure 1:- ribs
- intercostal spaces (spaces between the ribs)
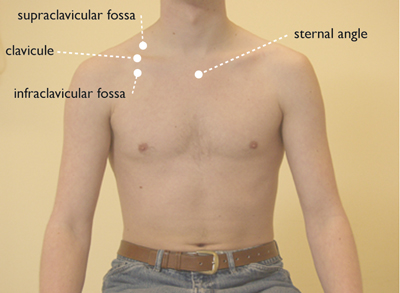 Figure 1: orientation points thoracic – anterior
Figure 1: orientation points thoracic – anterior
vertical (Figure 2)
- median line (through the middle of the sternum)
- parasternal line (directly next to the sternum)
- midclavicular line (through the middle of the clavicle)
- anterior axillary line (border between anterior and lateral side)
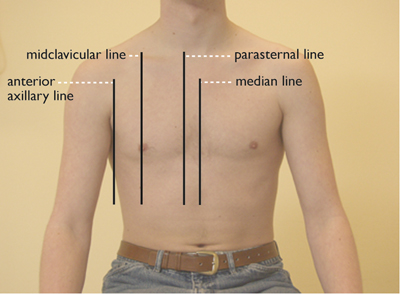 Figure 2: verticle orientation lines
Figure 2: verticle orientation lines
Posteriorly
horizontal (Figure 3)
- vertebra prominens (C7: 7th cervical vertebra)
- thoracic spinous processes (spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae)
- inferior scapular tip (lowest point of the shoulder blade)
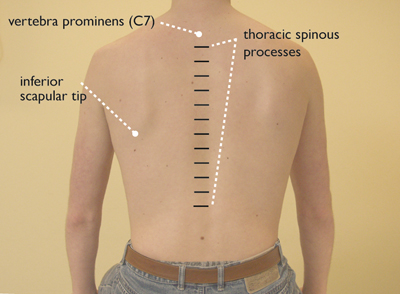 Figure 3: orientation points thoracic – posterior
Figure 3: orientation points thoracic – posterior
vertical (Figure 4)
- scapular line (through the inferior scapular tip)
- paravertebral line (directly next to the spine)
- spinal midline (through the middle of the spine)
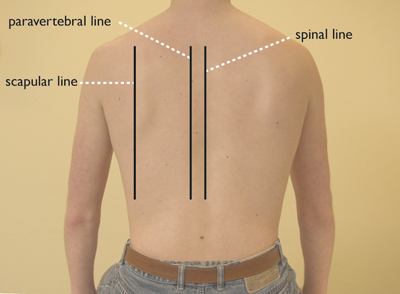 Figure 4: verticle orientation lines – posterior
Figure 4: verticle orientation lines – posterior
Laterally
horizontal (not indicated in a Figure)
- ribs
- intercostal spaces
vertical (Figure 5)
- anterior axillary line (border front and lateral side)
- midaxillary line (from the middle of the axilla)
- posterior axillary line (border back and lateral side)
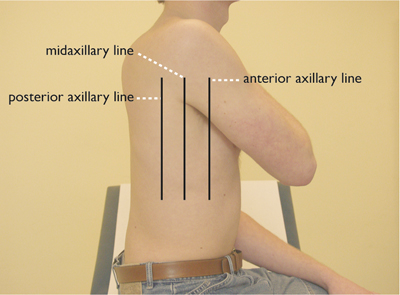 Figure 5: verticle orientation lines – lateral
Figure 5: verticle orientation lines – lateral




























